1. How do you communicate and manage stakeholders?
1. First of all I will determine Power-Interest position of the stakeholder in the matrix and keep them: Closely managed, Satisfied, Informed, Monitored.
- Power/interest - Closely manage
- Power/non-interest - Keep satisfied
- Non power/Interest - Inform
- Non-power/Non-interest - Monitor
2. Second I will adjust my communication style according to 4 types of people:
- ET - Controllers. Need quick updates, can't tolerate long meeting and details.
- IT - Analysts. Need detailed answers and lists.
- EF - Enthusiasts. They need the pitch to be motivating and fun.
- IF - Nice people. They need emotional rapport and connection.
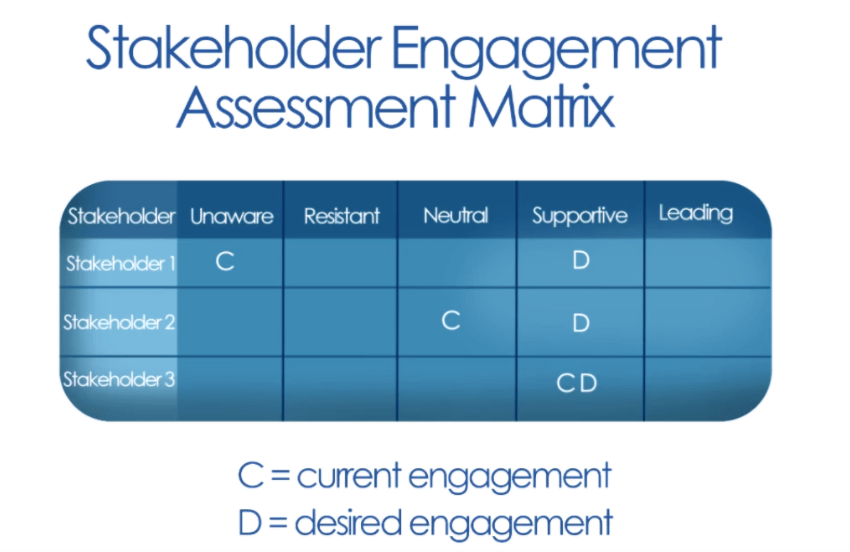
3. Third, I will use 'Stakeholder Engagement Asessment Matrix'. We have here 2 points: current position, desired position, and 5 states of stakeholder:
- Unaware
- Resistant
- Neutral
- Supportive
- Leading
The task is to plan and transfer stakholder from current position to desired.
2. How do you manage a project from the beginning to end?
No matter which framework you use, the process flow is as follows: initiation, planning, execution, monitor and control, closing.
3. What are the techniques you may use to define the scope of a project?
- Expert judgment: This involves seeking the advice of experts in the field to help you understand the requirements.
- Brainstorming: This is a group activity where participants generate ideas about a particular topic.
- Interviews: This is a one-on-one conversation with a user or stakeholder to gather information about their needs and expectations.
- Voting: This is a method for making decisions by having participants rank or vote on a set of options.
- Multicriteria decision analysis: This is a more complex method for making decisions that takes into account multiple factors, such as cost, time, and quality.
- Mind mapping: This is a technique for visualizing information by creating a diagram that shows the relationships between different concepts.
- Context diagram: This is a diagram that shows the relationship between the system and its environment.
- User journey mapping: This is a technique for understanding the user's experience with a system by mapping out their steps and interactions.
4. How will you avoid gold plating?
- Defining what should not be done as well with scope.
- Independent observers will be better to see the scope creep and gold plating.
5. How do you manage Schedule?
- Define activities
- Sequence activities
- Estimate activity durations (determine critical path)
- Develope schedule
- Control schedule
6. What are 3 main baselines of project management?
- Defining scope
- Create WBS (work breakdown structure)
- Monitor and control scope
- ---
- Define activities
- Create schedule
- Monitor and control schedule
- ---
- Define budget
- Track expenses
- Adjust budget
7. What KPIs do you gather?
Here are some main technical quality metrics often used in software development:
- Production incidents
- Time to restore the service
- Cyclomatic Complexity: Assesses the complexity of code by counting the number of independent paths through a function, helping identify potentially complex and hard-to-maintain areas.
- Code Coverage: Measures the percentage of code that is covered by automated tests, indicating the effectiveness of test suites in validating the codebase.
- Code Duplication: Identifies duplicated code segments within a codebase, highlighting potential maintenance issues and opportunities for code reuse and refactoring.
- Change failure rate
- Defect rate - Stories vs Defects
- Detected bugs vs Resolved bugs
- Broken builds
- Deployment frequency
8. What is DoR?
DoR stands for 'Definition of Ready' in Scrum. It is a set of criteria that a product backlog item must meet before it is deemed ready to be worked on by the development team.
It should comply with INVEST.
Every Product Backlog item should comply with DoR. This is done during Product Backlog Refinement. Product Backlog Refinement is an ongoing process during the sprint.
- A clear and concise description of the product backlog item.
- Acceptance criteria that define what needs to be done to consider the item complete.
- A prioritization of the item within the product backlog.
- Any dependencies or prerequisites that must be met before the item can be worked on.
- A clear understanding of the business value that the item delivers.
9. What are usual Release Procedures?
- Finalize release scope.
- Build and package.
- Deployment planning.
- User acceptance testing (UAT).
- Deployment.
- Post-release validation.
10. What is KANBAN?
Kanban is a visual framework used for managing and optimizing workflow. It originated from the manufacturing industry but has been widely adopted in software development and project management.
The key principles of Kanban are:
- Visualize Work: Represent work items on a Kanban board to provide visibility and transparency.
- Limit Work in Progress (WIP): Set explicit limits on the number of items allowed in each workflow stage to optimize flow and prevent overburdening the team.
- Manage Flow: Focus on achieving a smooth and continuous flow of work by identifying and addressing bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Make Policies Explicit: Clearly define and communicate the rules, policies, and procedures governing the workflow to ensure consistency and shared understanding.
- Improve Collaboratively, Evolve Experimentally: Encourage continuous improvement through collaboration and experimentation, seeking opportunities to refine processes and practices.
11. How do you work in Kanban?
- Kanban Board
- Kanban Cards
- WIP Limit
- Kanban Metrics
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
- Classes of Service (CoS)
- Policies and Feedback Loops
- Kanban System Design
- Kanban at Scale
- Kanban Maturity Model
12. What Tech metrics (quality, code) do you provide?
Here are some main technical quality metrics often used in software development:
- Production incidents
- Time to restore the service
- Cyclomatic Complexity: Assesses the complexity of code by counting the number of independent paths through a function, helping identify potentially complex and hard-to-maintain areas.
- Code Coverage: Measures the percentage of code that is covered by automated tests, indicating the effectiveness of test suites in validating the codebase.
- Code Duplication: Identifies duplicated code segments within a codebase, highlighting potential maintenance issues and opportunities for code reuse and refactoring.
- Change failure rate
- Defect rate - Stories vs Defects
- Detected bugs vs Resolved bugs
- Broken builds
- Deployment frequency
13. What is Technical debt?
The cost of maintaining and improving code that has been developed quickly and without following best practices.
- Refactoring: Allocate time and resources to refactor the codebase, improving its structure, readability, and maintainability. This involves identifying and addressing areas of poor design, code duplication, and outdated technologies.
- Prioritization: Prioritize technical debt items based on their impact on the project, considering factors such as business value, customer impact, and risk. This helps determine which areas should be addressed first to maximize the benefits of debt reduction.
- Prevention: Implement practices and processes to prevent the accumulation of new technical debt. This includes emphasizing code reviews, automated testing, and following coding standards to ensure that code is clean, efficient, and meets quality criteria.
14. What is SDLC?
SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) is a systematic process used in software development to design, develop, test, and deploy high-quality software applications. It provides a structured approach for managing and controlling the software development process, ensuring that software projects are completed efficiently and effectively.
- Planning: Defining the project scope, goals, and requirements, and creating a roadmap for the development process.
- Analysis: Gathering and analyzing user requirements, studying the existing system (if applicable), and identifying any potential risks or challenges. Getting client approved requirements.
- Design & Prototype: Creating a detailed design specification, including the software architecture, database structure, and user interface. Developing prototypes to validate the design and gather feedback.
- Development: Writing the actual code, implementing the software based on the design specifications, and integrating various components and modules.
- Testing: Conducting comprehensive testing, including unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing, to identify and fix any defects or issues.
- Launch (Deployment): Releasing the software application to end-users or customers, including installation, configuration, and final deployment.
- Maintenance: Providing ongoing support, bug fixes, updates, and enhancements to the software to ensure its optimal performance and functionality throughout its lifecycle.
15. How Deployment should be done?
Deployment should be done through the following steps:
- Build and package: Create a build of the software and package it into a deployable format, such as a binary or container image.
- Configure environments: Set up and configure the target deployment environments, including servers, databases, and any necessary infrastructure components.
- Automate deployment: Implement an automated deployment process using tools like continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. This ensures consistent and repeatable deployments.
- Test in staging: Deploy the software to a staging or pre-production environment and perform thorough testing to validate its functionality and compatibility.
- Monitor and rollback: Monitor the deployed application in the production environment, gathering metrics and monitoring for any issues. If necessary, be prepared to rollback to a previous version in case of problems.
- Document and communicate: Document the deployment process, including any specific steps or configurations, and communicate them to the team. This helps ensure consistency and facilitates future deployments.
16. What is Test-Driven Development?
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a software development approach that emphasizes writing tests before writing the actual code.
17. How do you get accurate estimates?
To get accurate estimates, you can follow these steps:
- Break down the task or project into smaller, more manageable components. And perform bottom-up estimation.
- Consider rought estimates first -25/+75
- Use Beta Distribution analysis
- Use analogous and parametric estimation from the historical data
- Account for potential risks and estimate 15% percent contingency resevere
- Regularly update estimates when new information becomes available